| |
|
Thermal
radiation - Within one millionth of a second from a detonation
in the atmosphere, about 35 percent of the energy of the bomb is emitted
in the form of thermal radiation which propagates itself at a speed
slightly below the speed of light. The heat generated which at the center
of the fireball reaches a temperature of 10 million degrees
centigrade, is emitted from the extremely hot residues of the nuclear
weapon which contribute to the formation of the extremely luminous sphere
of gases and hot air. After only 700 microseconds the fireball
generated from the explosion of a 1-megaton bomb will have
a diameter of approximately 134 meters; the maximum diameter, 2,240
meters, will be obtained in approximately 10 seconds. To an observer
at a distance of 80 kilometers from the explosion's site, in favorable
visibility conditions, the fireball generated from such an
explosion would appear many times more brilliant that the sun at noon.
The surface temperature of the fireball does not change greatly
in relation to the power of the weapon while the same cannot be said
for the thermal radiation since its ray of action is increased in relation
to the increased power of the weapon hence the distance of thermal radiation
is proportional to the explosive power of the weapon. Haze, fog and
smog may greatly contribute to attenuate both the optical and the thermal
effects which, however, with good visibility extend beyond the ray of
action of the ionizing radiation and of the blast wave. As
well, the geomorphological conformation of the area is also important
in this respect as related to the altitude of burst of the weapon.
|
|
|
|
|
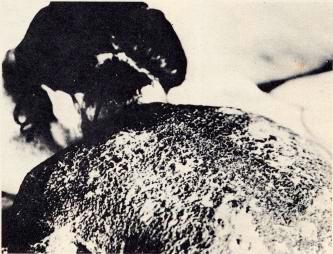
This women suffered serious burns on the back . Hiroshima - Masayoshi
Onuka, HNPC) |
The
explosion of a nuclear weapon of 25 megaton may cause, in good
visibility conditions, serious burns to exposed parts of the
body at a distance in excess of 40 kilometers from the epicenter
while the same effect with a 1-megaton bomb in analogous atmospheric
circumstances will obtain at a distance of 11 kilometers.The
lethality index from burns is thus related to the weapon's power
and the atmospheric conditions; it is estimated that an exposition
of the body in excess of 6.7 calories per square centimeter
is lethal while an exposition in excess of 3.4 calories per
square centimeter will cause considerable burns which will require
specialized medical care.
Nuclear
(or Ionizing) Radiation -The electromagnetic spectrum
consists, in this sequence, of cosmic rays, gamma rays, X rays,
ultraviolet radiations, visible light, infrared radiation and
radio waves (see figure 1.74 on previous
page). These radiations are all similar from the standpoint
that they have no mass or substance and technically they are
different only for their different wavelength and each produces
different effects.
•
PREVIOUS •
NEXT
|
|
